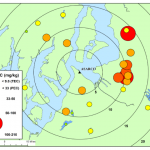
Arsenic mobility and bioavailability in South King County lakes
by Jim Gawel, Ph.D., Erin Hull, Marco Barajas, Ken Burkart, Rebecca Neumann, Ph.D., Alex Horner-Devine, Ph.D., and Samantha Fung
Arsenic, a priority Superfund contaminant and carcinogen, is a legacy pollutant impacting aquatic ecosystems in urban lakes downwind of the former American Smelting and Refining Company (ASARCO) copper smelter in Ruston, WA, now designated as the Commencement Bay/Nearshore Tideflats Superfund Site. A majority of Superfund sites are located in densely-settled areas; nationally, 139 of these sites have arsenic-contaminated surface waters. However, the human health and ecological implications of arsenic contamination are unclear due to an incomplete understanding of arsenic bioavailability in urban waters.
Register now to return to Lake Chelan for the 32nd Annual WALPA Conference!
“Lakes are for Everyone”
 We’re just a couple of months away from our 2019 conference – you won’t want to miss enjoying beautiful Lake Chelan in the fall at Campbell’s Resort! This location has been a hit for our conferences in the past and we are excited to return this year for what is sure to be an enjoyable and informative annual meeting. Please join us from October 30th through November 1st for a program full of sessions, workshops, and socializing with fellow lake lovers.
We’re just a couple of months away from our 2019 conference – you won’t want to miss enjoying beautiful Lake Chelan in the fall at Campbell’s Resort! This location has been a hit for our conferences in the past and we are excited to return this year for what is sure to be an enjoyable and informative annual meeting. Please join us from October 30th through November 1st for a program full of sessions, workshops, and socializing with fellow lake lovers.
HABs (Harmful Algal Blooms) in lakeshore sediments: A human health issue?
by Joan Hardy, Will Hobbs, & Ellen Preece
 People want to swim in lakes and play on lake beaches, but these days they have to check for algae blooms before jumping in since cyanobacteria can produce toxins that could harm lakes users. Primary exposure routes are through accidental ingestion of water during recreational activities and contaminated drinking water from public water systems that do not adequately remove cyanotoxins. In Washington, cyanotoxins have been documented in many recreational lakes throughout the state, the most prevalent of which are the liver toxins microcystins (MCs).
People want to swim in lakes and play on lake beaches, but these days they have to check for algae blooms before jumping in since cyanobacteria can produce toxins that could harm lakes users. Primary exposure routes are through accidental ingestion of water during recreational activities and contaminated drinking water from public water systems that do not adequately remove cyanotoxins. In Washington, cyanotoxins have been documented in many recreational lakes throughout the state, the most prevalent of which are the liver toxins microcystins (MCs).
Exploring the connection between summer stratification and methane dynamics in a eutrophic lake
Sofia D’Ambrosio, Ph.D. Candidate, Washington State University Vancouver
 Lakes and reservoirs are a significant source of methane (CH4), a potent greenhouse gas with important global effects on climate (Bastviken et al. 2004; Deemer et al. 2016; St. Louis et al. 2000). In lakes, microbes produce CH4 during decomposition of organic matter in low-oxygen, carbon-rich sediments. Bacteria consume some produced CH4 via a microbial process called CH4 oxidation. However, a significant amount of CH4 avoids oxidation and is ultimately emitted to the atmosphere. Given that the balance between CH4 production and oxidation ultimately determines CH4 emission, understanding environmental controls on both processes is a critical step towards accurately estimating greenhouse gas emissions from lakes.
Lakes and reservoirs are a significant source of methane (CH4), a potent greenhouse gas with important global effects on climate (Bastviken et al. 2004; Deemer et al. 2016; St. Louis et al. 2000). In lakes, microbes produce CH4 during decomposition of organic matter in low-oxygen, carbon-rich sediments. Bacteria consume some produced CH4 via a microbial process called CH4 oxidation. However, a significant amount of CH4 avoids oxidation and is ultimately emitted to the atmosphere. Given that the balance between CH4 production and oxidation ultimately determines CH4 emission, understanding environmental controls on both processes is a critical step towards accurately estimating greenhouse gas emissions from lakes.
Join the WALPA Board!

Becoming a WALPA officer or Board member allows you to play a key role in our efforts to expand and improve lake management and protection practices in Washington State, network with limnological professionals throughout the Pacific Northwest, and take an active part in planning and executing our annual conference (as well as interact with a downright lovely group of people).
SLMP seeking applications for student scholarships
![]() The Society of Lake Management Professionals (SLMP) is seeking applications for its annual Student Scholarship Award. SLMP intends to award $3,500 in scholarships to the successful applicants at the January 2020 SLMP Summit that will take place January 20- 23, 2020 in St. Petersburg, Florida.Scholarship funds are provided directly to the student and may be used by the recipient to cover costs associated with education and research. Eligible applicants must be enrolled as full-time undergraduate or graduate students in an accredited college or university in the United States. Coursework or research in an area related to water quality, aquatic plant management, fisheries management, or aquatic ecology of impounded waters is required.
The Society of Lake Management Professionals (SLMP) is seeking applications for its annual Student Scholarship Award. SLMP intends to award $3,500 in scholarships to the successful applicants at the January 2020 SLMP Summit that will take place January 20- 23, 2020 in St. Petersburg, Florida.Scholarship funds are provided directly to the student and may be used by the recipient to cover costs associated with education and research. Eligible applicants must be enrolled as full-time undergraduate or graduate students in an accredited college or university in the United States. Coursework or research in an area related to water quality, aquatic plant management, fisheries management, or aquatic ecology of impounded waters is required.
What drives resource integration in lakes?
by Beka Stiling, MS candidate, School of Aquatic and Fishery Sciences, University of Washington
Evidence suggests that the integration of energetic pathways via the transfer of resources across habitat boundaries can influence community structure, maintain species biomass, and promote food web stability. Despite our ability to measure resource integration, we do not have a strong understanding of the factors that determine the varying degrees of resource integration that we observe in fish.